Human-Relevant Training Methods
Since the 1990s, hundreds of medical schools and hospitals have replaced animals in training programs with methods based on human anatomy and physiology. These methods allow trainees to improve their skills through repetitive practice. Improvements in artificial tissues, new techniques for turning human cadavers into lifelike models, and an ethical imperative to reduce and replace animals in medical training have led to a new era in medical simulation. Here we highlight a few of the many simulation devices available to replace animals.
TraumaMan System
Simulab
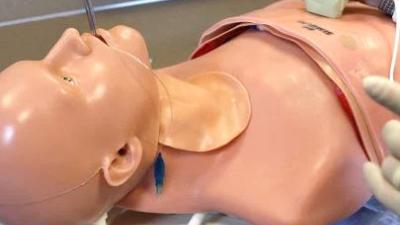
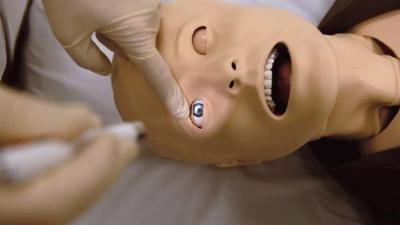
The most widely used trauma and surgical simulator in the world, the TraumaMan System is a high-fidelity human-body mannequin with lifelike skin, subcutaneous fat, and muscle. TraumaMan allows students to practice a variety of surgical procedures, such as cricothyroidotomy, chest tube placement, needle decompression, pericardiocentesis, intravenous cutdown, diagnostic peritoneal lavage, and ultrasound-guided interventions. Replaceable tissues provide each trainee with a first-cut experience and make this simulator ideal for team training scenarios.
SimMan 3G Plus
Laerdal
SimMan 3G Plus is a high-fidelity, full-body patient simulator that displays both physiological fidelity and pathology, with interchangeable head skins and realistic articulation. It can be used to teach numerous procedures, including cricothyroidotomy, chest tube placement, bleeding and hemorrhage control, endotracheal intubation, retrograde intubation, intraosseous needle insertion, intravenous insertion, and urinary catheterization. SimMan 3G Plus can be programmed to simulate a multitude of scenarios requiring defibrillation, cardiac pacing, and the administration of cardiac medications.
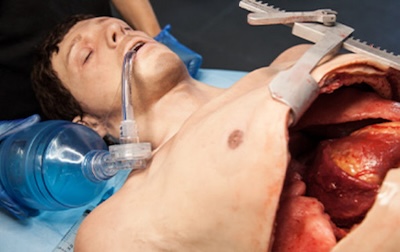
Human Worn Partial Task Surgical Simulator (a.k.a. “Cut Suit”)
Strategic Operations
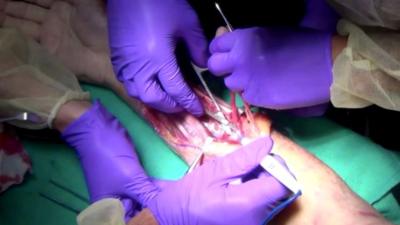
The Cut Suit is a surgical training device worn by a course participant or actor which features breakable bones, interchangeable organs, and variable blood flow. It combines the sensation of working on live tissue with the realism of performing emergency assessment and treatment on a live patient. Wounds are created by the user, and the skin and other organs are repairable, allowing for multiple uses and team training opportunities. The Cut Suit can be used to practice open thoracotomy and intrathoracic exploratory surgery, hemorrhage control of gross organ structures, chest tube placement, cricothyroidotomy, and urinary catheterization. The Cut Suit can be used to practice open thoracotomy and intrathoracic exploratory surgery, hemorrhage control of gross organ structures, chest tube placement, cricothyroidotomy, Foley catheterization, anastomosis and resection, and intravenous access.
EnvivoPC Perfused Cadaver
Maximum Fidelity Surgical Simulations, LLC
The EnvivoPC simulator uses state-of-the-art technology—including simulated blood and a pump—to create a perfused cadaver that mimics heart function and circulation while allowing for hands-on training of procedures involving active bleeding. EnvivoPC can be used to perform a variety of medical procedures, including chest tube placement, cricothyroidotomy, central line placement, venous and arterial cutdown, open thoracotomy, hemorrhage control, and cardiac repair.
Tactical Casualty Care Simulator Plus Pro
Operative Experience, Inc.
The Tactical Casualty Care Simulator (TCCS) Plus Pro is a high-fidelity, full-body patient simulator designed for prolonged field care training. With lifelike soft tissue and skin, this simulator can be used to practice cricothyroidotomy, difficult airway with tongue swelling, chest tube placement, and urinary catheterization. The TCCS also features the ability to assess and treat penetrating woods, amputation, and remote-controlled bleeding and heart rate. The TCCS Pro Smart Limbs have fully interchangeable trauma wound configurations with corresponding software that automatically adjusts to specific limb features.
Thoracotomy Half Body Task Trainer
SIMBODIES
The Thoracotomy Half Body Task Trainer is a high-fidelity simulator that features lifelike skin and fat, a thoracic skeleton with a replaceable sternum, and a manually pumped heart and pericardium. This task trainer can be used to teach open thoracotomy, chest tube placement, needle thoracentesis, nasopharyngeal airway insertion, oropharyngeal airway insertion, supraglottic airway device insertion, laryngoscopy/tracheal intubation, cardiopulmonary resuscitation, and intraosseous access.
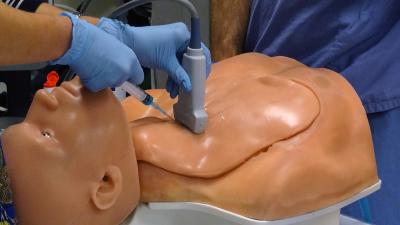
CentraLineMan
Simulab
CentraLineMan is a high-fidelity, partial-body simulator with an optional articulating head and replaceable tissues available to simulate a variety of patients (i.e., average, obese, and those with anatomical anomalies). It is the most widely used central venous catheterization simulator and allows trainees to practice vascular catheterization using ultrasound-guided or landmark-directed insertion. Repetition and iterative learning are important features.
BabySIM
Elevate Healthcare (formerly CAE Healthcare)
BabySIM is an infant-sized, high-fidelity simulator featuring advanced physiology for trauma management and critical care. Trainees can experience seesaw breathing, cooing, crying, variable pupil size, and secretions from the ears, eyes, and mouth. It provides simulation scenarios for airway trauma or obstruction, defibrillation and cardiac pacing, needle decompression, chest tube placement, and intraosseous insertion.
LAP Mentor
Surgical Science
LAP Mentor is a laparoscopic simulator with haptic feedback that allows trainees to practice a variety of techniques, from essential laparoscopic skills to advanced procedures. LAP Mentor can be used to teach basic and advanced suturing, incisional and inguinal hernia repair, nephrectomy, cholangiography, cholecystectomy, gastric bypass, lobectomy, hysterectomy, appendectomy, and Nissen fundoplication.
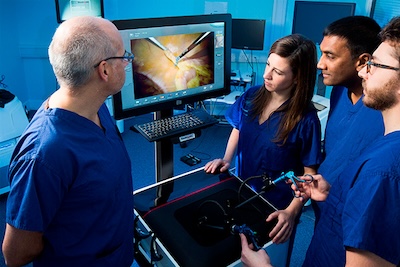
RobotiX Mentor
Surgical Science
The RobotiX Mentor is a state-of-the-art simulation platform for the training of robotic assisted surgery. It allows surgeons of all expertise levels to effectively practice the motor and cognitive skills required to perform robotic surgery. RobotiX can be used to teach cholecystectomy, inguinal hernia, hysterectomy, prostatectomy, right hemicolectomy, lobectomy, and basic suturing and stapling skills.
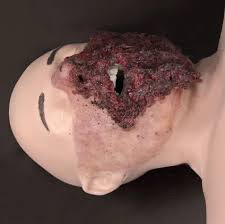
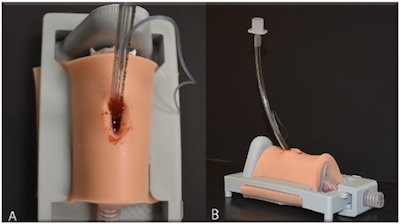
3D-Printed Simulators
Various
Around the world, medical centers are creating their own simulators using 3D printers. Above is a device created by emergency medicine faculty at the University of Arizona. It replicates the human airway and bleeds. In a 2018 study involving emergency medicine residents, the 3D-printed model “was rated higher than the previously used models,” including pigs, and participants “specifically commented on the realism of the bleeding tissue and texture of the skin” when performing surgical airway.